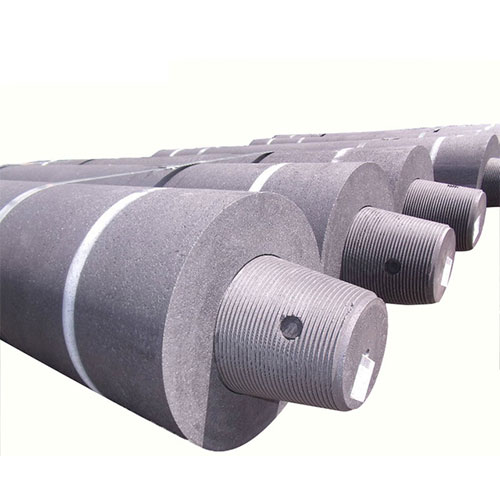
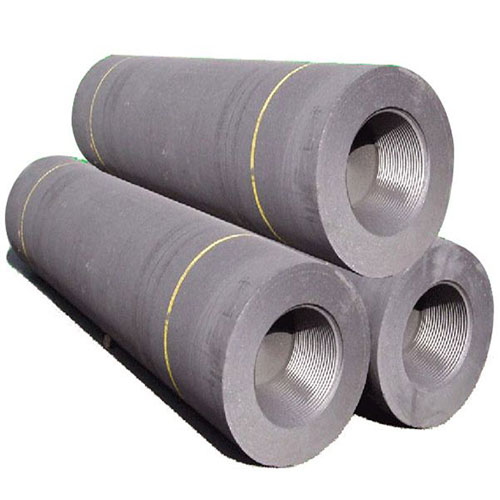
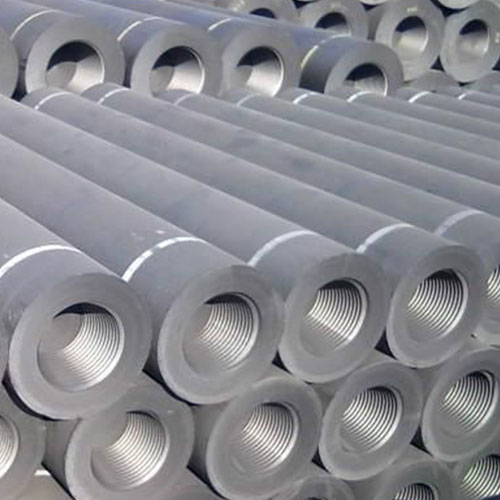
Graphite Electrode
1.Low electric resistance,
2.High density,
3.High anti-oxidation capability,
4.Precise machining accuracy.
Description
Inquiry
Related products
Description
Description of Graphite ElectrodeThe graphite electrode will be a high-temperature graphite conductive material, the core of which consists of petroleum coke, tar coke as a filler, coal tar as a binder. We produce graphite electrodes and nipples to them. Graphite electrodes are characterized by low resistance, good electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, high resistance to oxidation and thermal shock, high mechanical strength, etc.
Catalogue
★ Graphite Electrode Application
★ Classification of Graphite Electrodes
★ Graphite Electrodes Product Photos
★ The Length & Diameter & Permissible Deviation of Graphite Electrode
★ Technical Characteristics of Graphite Electrode RP, HP, UHP
★ Technical Characteristics of High Density Graphite Electrode (HD)
★ Technical Characteristics of a Quasi-Superhigh-Gauge Graphite Electrode (EGPK-SHP)
★ Advantages of Graphite Electrode
★ Use of Graphite Electrode
★ Our Suggestions before Connecting the Electrode
★ When Connecting the Electrodes, Please Note
★ Graphite Electrode Application
★ Graphite Electrode Application
1 for EAF arc furnace;
2 for ore-thermal furnace; for the resistance furnace;
3 for the production of profiled graphite products;
4 for the production of shaped graphite products.
Diameter of electrodes: from 75 to 800mm. We can produce various specifications in accordance with customer requirements.
Our advantages: Manufacturer from China; Buy directly from the factory; High-quality products; Profitable price.
★ Classification of Graphite Electrodes




★ The Length & Diameter & Permissible Deviation of Graphite Electrode
| Nominal Diameter | Actual Diameter | Length (mm) | Tolerance | ||||
| MM | Inch | Poppy | Mines | The Minimum Size Of The Black Part | Length | Short Length | |
| 75 | 3 | 78 | 73 | 72 | 1400/1600 | ± 100 | -275 |
| 100 | 4 | 103 | 98 | 97 | 1400/1600 | ||
| 130 | 5 | 132 | 127 | 126 | 1400 | ||
| 150 | 6 | 154 | 149 | 146 | 1400/1600/1800 | ||
| 175 | 7 | 180 | 174 | 172 | 1400/1600 | ||
| 200 | 8 | 205 | 200 | 197 | 1600/1800 | ||
| 225 | 9 | 230 | 225 | 222 | 1600/1800 | ||
| 250 | 10 | 255 | 251 | 248 | 1600/1800 | ||
| 300 | 12 | 307 | 302 | 299 | 1600/1800/2000 | ||
| 350 | 14 | 357 | 352 | 349 | 1600/1800/2000 | ||
| 400 | 16 | 409 | 403 | 400 | 1600/1800/2000/22000 | ||
| 450 | 18 | 460 | 454 | 451 | 1600/1800/2000/22000 | ||
| 500 | 20 | 511 | 505 | 502 | 1600/1800/2000/22000 | ||
| 550 | 22 | 562 | 556 | 553 | 1800/2000/2200/2400 | ||
| 600 | 24 | 613 | 607 | 604 | 2000/2200/2400/2700 | ||
| 650 | 26 | 663 | 659 | 656 | 2000/2200/2400/2700 | ||
| 700 | 28 | 714 | 710 | 707 | 2000/2200/2400/2700 | ||
★ Technical Characteristics of Graphite Electrode RP, HP, UHP
| Name | Unit | Nominal Diameter | ||||||
| UHP Ultra-High-Power | HP Superstrong | RP Conventional Power | ||||||
| ≤Φ400 | ≥Φ450 | ≤Φ400 | ≥Φ450 | ≤Φ300 | ≥Φ350 | |||
| Resistivity | Electrode | ΜΩ · m | ≤5.5 | ≤6.5 | ≤8.5 | |||
| Nipple | ≤4.5 | ≤5.5 | ≤6.5 | |||||
| Flexural Strength | Electrode | MPa | ≥11.0 | ≥10.5 | ≥9.8 | ≥8.5 | ≥7.0 | |
| Nipple | ≥20.0 | ≥16.0 | ≥15.0 | |||||
| Elastic Modulus | Electrode | GPa | ≤14.0 | ≤12.0 | ≤9.3 | |||
| Nipple | ≤18.0 | ≤16.0 | ≤14.0 | |||||
| Density | Electrode | g / cm3 | ≥1.66 | ≥1.67 | ≥1.62 | 1.6 | ≥1.53 | ≥1.52 |
| Nipple | ≥1.75 | ≥1.73 | ≥1.69 | |||||
| Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion | Electrode | 10-6 / ℃ | ≤1.5 | ≤2.4 | ≤2.9 | |||
| Nipple | ≤1.4 | ≤2.2 | ≤2.8 | |||||
| ASH | % | ≤0.3 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.5 | ||||
| Note: 1.Koeffitsient ash content and thermal expansion as the reference index, the coefficient of thermal expansion (100 ℃ ~ 600 ℃), Custom manufacturing. | ||||||||
★ Technical Characteristics of High Density Graphite Electrode (HD)
★ Technical Characteristics of a Quasi-Superhigh-Gauge Graphite Electrode (EGPK-SHP)
| Name | Unit | Nominal Diameter (mm) | ||
| 300, 350, 400 | 450, 500 | |||
| Resistivity (not more than) | Electrode | ΜΩ · m | 6.2 | 6.5 |
| Nipple | 5.5 | 5.5 | ||
| Flexural Strength(not less than) | Electrode | MPa | 10.5 | 10 |
| Nipple | 16 | 16 | ||
| Elastic Modulus(no more) | Electrode | GPa | 14 | 14 |
| Nipple | 18 | 18 | ||
| Density(not less than) | Electrode | g / cm3 | 1.65 | 1.64 |
| Nipple | 1.72 | 1.7 | ||
| Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion (no more) | Electrode | 10-6 / ℃ | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Nipple | 1.4 | 1.4 | ||
| Ash Content (not more than) | % | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Note: 1. Zonality as a reference index. | ||||
If you have any requirements, please Contact Us. Our engineers will help you and provide appropriate advice.
★ Advantages of Graphite Electrode
1 The process of graphite electrode production is simple, high efficiency, small graphite loss
2 Fast processing speed, lower production costs
3 Different sizes available, including large diameter
4 Our graphite electrodes are very durable and have a long service life
★ Use of Graphite Electrode
1 For arc furnaces of electric arc furnaces. Graphite electrodes are most often used in a coal-smelting electric furnace.
2 For a closed arc
3 For a resistor furnace
4 For the production of graphite shaped products. The graphite electrode blank is also used for processing in various crucibles, shapes, boats and heating elements and other graphite products. For example, in the quartz glass industry, for each production of 1 ton of an electric melting tube, a graphite electrode 10 m is required, for each quartz brick of 1 ton it is necessary to consume 100 kg of graphite electrode.
★ Our Suggestions before Connecting the Electrode
1 Please check the internal thread of the electrode first. If the thread is not intact, please contact sales staff to confirm whether the electrode can work properly.
2 Please clean the electrodes with compressed air before connecting.
3 When the electrode is squeezed into the electrode hole at one end, the pad can be prepared at the other end to avoid nipple breakage.
★ When Connecting the Electrodes, Please Note
1 drop down slowly when the new electrode is directly above the hole connected to the electrode.
2 put the insulator between the two electrodes, and the electrode drop slowly to prevent the electrode hole breakage and nipple threads.
3 Raise the new electrode slightly, and then remove the insulator, connect the two electrodes.
4 Tighten the electrodes with a proper wrench and specified torque.
Request For Quotation
You can get the price list and we will contact you within one working day.
+86 13526662273
Case

Our Refractory Bricks Are Exported to Egypt

GIFA 2019

Great Job Done for South Africa Customer

South Korean Customer and Indonesian Customer Visit
Are you interested in our offer?
Contact us!10th Floor, No. 6 Building, China Central Electronic CommercePort Daxue Road, Zhengzhou, Henan
Copyright @ ZHENGZHOU RONGSHENG REFRACTORY CO., LTD. All rights reserved site map/site index